
Since the larger square has sides c and area c 2, the above can be rewritten as: The area of the larger square must then equal the sum of the areas of the four triangles and the smaller square such that: (b - a) 2 + 4

The four triangles with area abĪlso form a larger square with sides of length c. In the second orientation shown in the figure, ii, the four copies of the same triangle are arranged such that they form an enclosed square with sides of length b - a, and area (b - a) 2. The sum of the area of these four triangles and the smaller square must equal the area of the larger square such that: (b + a) 2 = c 2 + 4 This results in the formation of a larger square with sides of length b + a, and area of (b + a) 2. In the first one, i, the four copies of the same triangle are arranged around a square with sides c. In the figure above, there are two orientations of copies of right triangles used to form a smaller and larger square, labeled i and ii, that depict two algebraic proofs of the Pythagorean theorem. There are a multitude of proofs for the Pythagorean theorem, possibly even the greatest number of any mathematical theorem. If the angle between the other sides is a right angle, the law of cosines reduces to the Pythagorean equation. The law of cosines is a generalization of the Pythagorean theorem that can be used to determine the length of any side of a triangle if the lengths and angles of the other two sides of the triangle are known. It follows that the length of a and b can also be determined if the lengths of the other two sides are known using the following relationships:

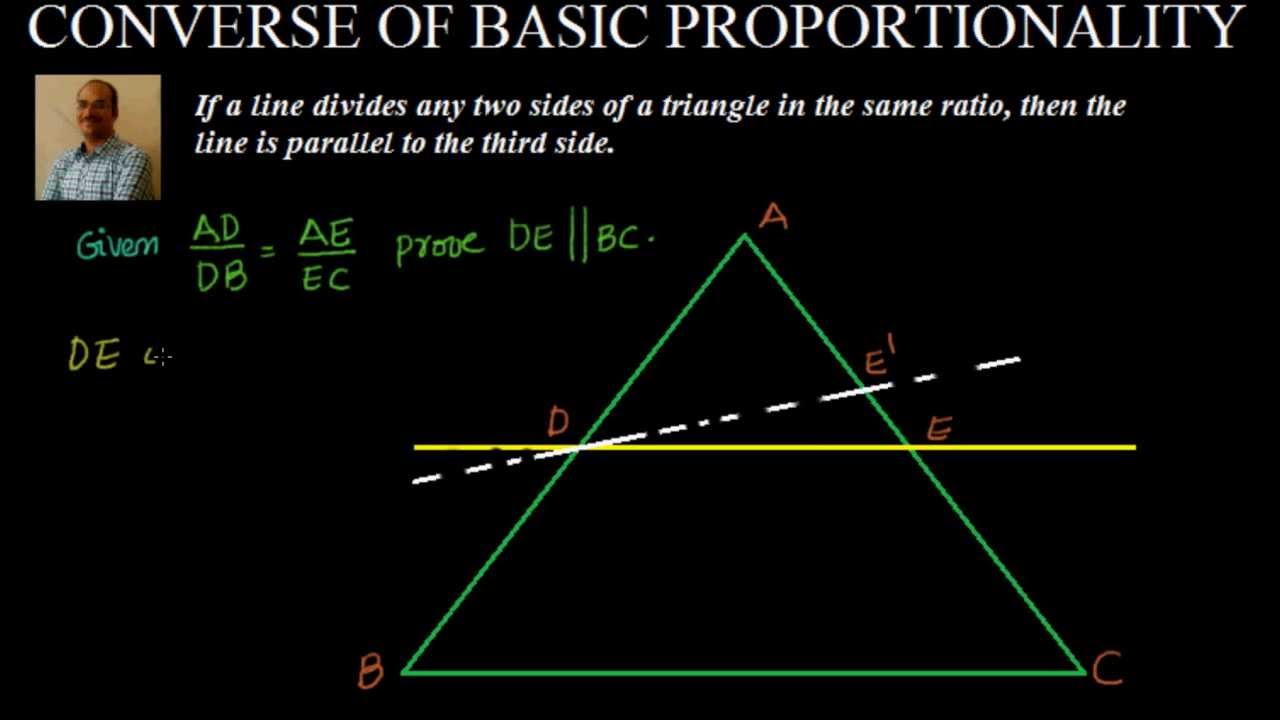
This relationship is useful because if two sides of a right triangle are known, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to determine the length of the third side. This is known as the Pythagorean equation, named after the ancient Greek thinker Pythagoras. In other words, given that the longest side c = the hypotenuse, and a and b = the other sides of the triangle: Given a right triangle, which is a triangle in which one of the angles is 90°, the Pythagorean theorem states that the area of the square formed by the longest side of the right triangle (the hypotenuse) is equal to the sum of the area of the squares formed by the other two sides of the right triangle: The Pythagorean Theorem, also known as Pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation between the three sides of a right triangle. Columbia University.Related Triangle Calculator | Right Triangle Calculator “Private tutoring and its impact on students' academic achievement, formal schooling, and educational inequality in Korea.” Unpublished doctoral thesis.
#Converse geometry triangles professional
Tutors, instructors, experts, educators, and other professionals on the platform are independent contractors, who use their own styles, methods, and materials and create their own lesson plans based upon their experience, professional judgment, and the learners with whom they engage. Varsity Tutors connects learners with a variety of experts and professionals. Varsity Tutors does not have affiliation with universities mentioned on its website. Media outlet trademarks are owned by the respective media outlets and are not affiliated with Varsity Tutors.Īward-Winning claim based on CBS Local and Houston Press awards. Names of standardized tests are owned by the trademark holders and are not affiliated with Varsity Tutors LLC.Ĥ.9/5.0 Satisfaction Rating based upon cumulative historical session ratings through 12/31/20.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
